Searchable Database of Pan-Gene Family Members Involved in Ascorbic Acid Metabolism
L-ascorbic acid (AsA), also known as vitamin C, plays a crucial role in plant growth and development. As an important antioxidant, AsA not only helps maintain redox balance and resist both biotic and abiotic stresses, but also regulates plant growth, induces flowering, and delays senescence through complex signal transduction networks. AsA metabolism is a complex physiological process involving a series of functional genes. Systematic identification of genes related to AsA metabolism across multiple species is of great significance for understanding the mechanisms underlying AsA accumulation in organisms and for enhancing AsA content in plants and animals through genetic engineering.
To meet the needs of researchers for information on these genes, reduce the workload of identifying AsA-related genes, and avoid confusion in gene nomenclature, we have developed the “Ascorbic Acid Metabolic Gene Homolog Retrieval Database.” This website identifies the gene family members of 17 AsA metabolic genes across 21 species, including Arabidopsis thaliana, tomato, grape, Actinidia chinensis cv ‘Hongyang’, cv ‘Red5’, and cv ‘Donghong’, wild Actinidia eriantha, A. eriantha cv ‘White’ and cv ‘Ganlv 1’, A. latifolia, A.rufa, apple, pear, peach, Rosa roxburghii cv ‘Guinong 5’, jujube, sweet orange, pomelo, ponkan, trifoliate orange, and citron. Each gene family member is named according to its order on the chromosome and has a dedicated subpage. Researchers can obtain homologous genes of a given AsA metabolic gene across the 21 species and directly download the corresponding protein sequences by clicking “Download” on the main page.
Please do not use this database for commercial purposes or genomic analysis!
If you used the data from the database, please cite the paper kindly!
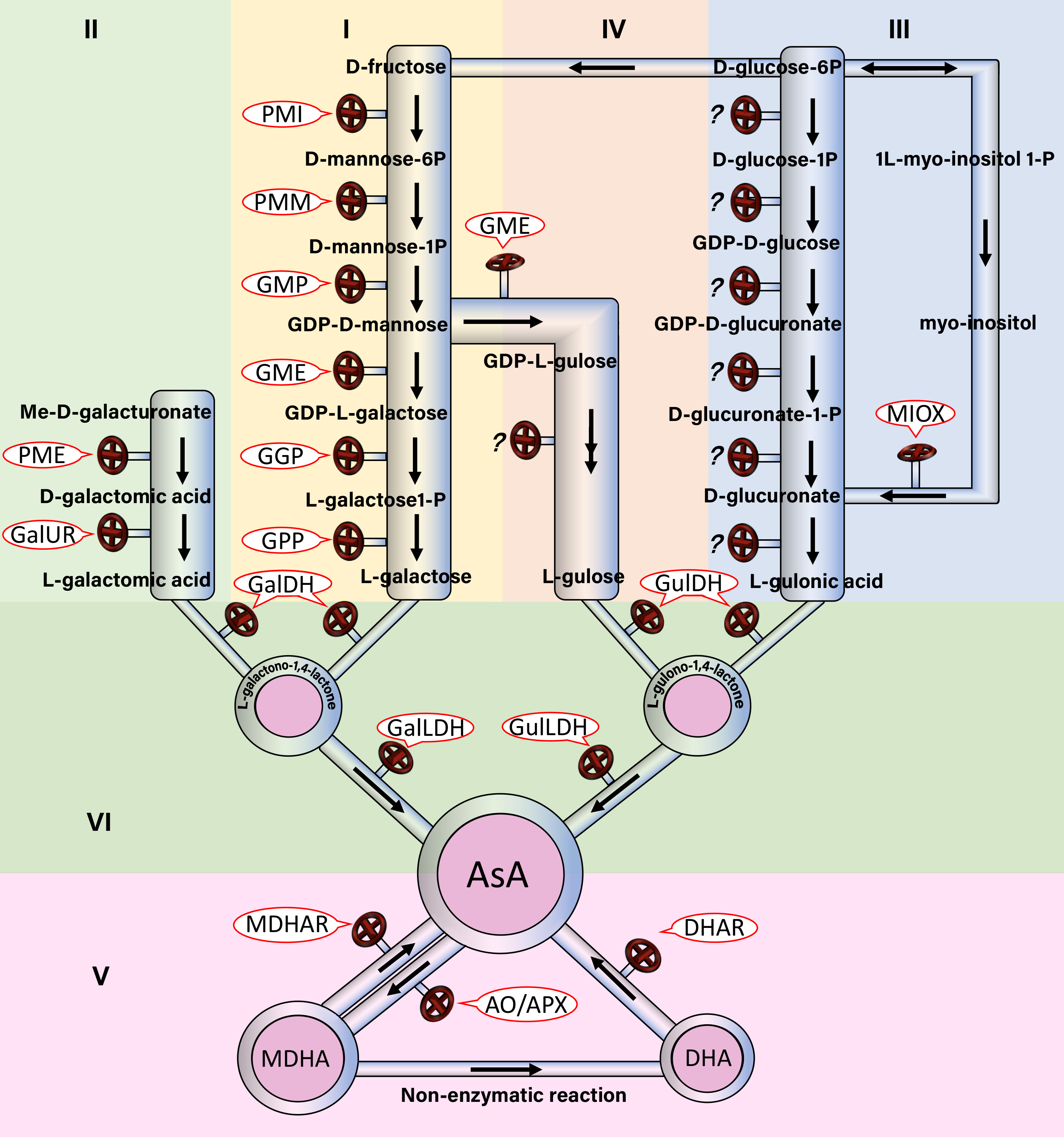
Ⅰ The L-galactose pathway : PMI,PMM,GMP,GME,GGP,GPP
Ⅱ The D-galacturonic acid pathway : PME,GaIUR
Ⅲ The inositol pathway :MIOX
Ⅳ The L-gulose pathway :Has not been identified yet!
Ⅴ The cyclic regeneration pathways :MDHAR,DHAR
Ⅵ The degradation pathway:AO/APX
Ⅶ The commen pathway:GaIDH,GalLDH
Released Jun. 2025 | Developed by: Institute of Kiwifruit, JiangXi Agricultural University | Copyright © 2025~2027 . All rights reserved.